You are given a 0-indexed n x n grid where n is odd, and grid[r][c] is 0, 1, or 2.
We say that a cell belongs to the Letter Y if it belongs to one of the following:
- The diagonal starting at the top-left cell and ending at the center cell of the grid.
- The diagonal starting at the top-right cell and ending at the center cell of the grid.
- The vertical line starting at the center cell and ending at the bottom border of the grid.
The Letter Y is written on the grid if and only if:
- All values at cells belonging to the Y are equal.
- All values at cells not belonging to the Y are equal.
- The values at cells belonging to the Y are different from the values at cells not belonging to the Y.
Return the minimum number of operations needed to write the letter Y on the grid given that in one operation you can change the value at any cell to 0, 1, or 2.
Example 1:
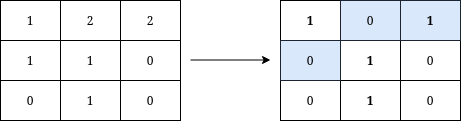
Input: grid = [[1,2,2],[1,1,0],[0,1,0]]
Output: 3
Explanation: We can write Y on the grid by applying the changes highlighted in blue in the image above. After the operations, all cells that belong to Y, denoted in bold, have the same value of 1 while those that do not belong to Y are equal to 0.
It can be shown that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed to write Y on the grid.
Example 2:

Input: grid = [[0,1,0,1,0],[2,1,0,1,2],[2,2,2,0,1],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,1,2,2,2]]
Output: 12
Explanation: We can write Y on the grid by applying the changes highlighted in blue in the image above. After the operations, all cells that belong to Y, denoted in bold, have the same value of 0 while those that do not belong to Y are equal to 2.
It can be shown that 12 is the minimum number of operations needed to write Y on the grid.
출처 : https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-operations-to-write-the-letter-y-on-a-grid/description/
풀이
function minimumOperationsToWriteY(grid: number[][]): number {
const cntY = Array(3).fill(0), cntX = Array(3).fill(0), n = grid.length - 1, n2 = n / 2;
// count whole grid
for (let x = 0; x <= n; x++)
for (let y = 0; y <= n; y++)
cntX[grid[y][x]]++;
// count Y only
cntY[grid[n2][n2]]++;
for (let i = 0; i < n2; i++)
cntY[grid[i][i]]++,
cntY[grid[i][n - i]]++,
cntY[grid[n - i][n2]]++;
// subtract Y from the grid
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) cntX[i] -= cntY[i];
const max = Math.max(
cntY[0] + cntX[1], cntY[0] + cntX[2],
cntY[1] + cntX[0], cntY[1] + cntX[2],
cntY[2] + cntX[0], cntY[2] + cntX[1],
)
return (n + 1) ** 2 - max;
};
주어진 grid에서 'Y' 모양을 그리기 위해 최소한의 변경 작업을 계산하는 함수
1. 초기 변수 설정
- cntY와 cntX는 각각 3개의 요소를 가진 배열로 초기화
- cntY는 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 필요한 숫자들의 개수를 저장하고, cntX는 전체 그리드에서의 숫자들의 개수를 저장
- n은 그리드의 크기를 나타내며, n2는 그리드 크기의 절반을 나타냄
2. 전체 그리드 숫자 개수 카운팅
- 중첩된 for 루프를 사용하여 그리드의 모든 요소를 순회하며 각 숫자의 개수를 cntX 배열에 저장
3. 'Y' 모양의 숫자 개수 카운팅
- 'Y' 모양은 그리드의 중앙 요소와 대각선 요소들, 그리고 그리드의 상반부에 있는 세로 줄의 요소들을 포함
- 중앙 요소의 숫자 개수를 증가
- 대각선 요소들과 세로 줄의 요소들의 숫자 개수를 카운팅하여 cntY 배열에 저장
4. 'Y' 모양의 숫자 개수를 전체 그리드 숫자 개수에서 차감
- 'Y' 모양에 사용된 숫자들을 전체 그리드 숫자 개수에서 차감합니다.
5. 최소 변경 작업 계산
- 'Y' 모양을 그리기 위해 필요한 변경 작업의 최소 개수를 계산.
- 이는 'Y' 모양에 사용되지 않은 숫자들을 이용하여 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 필요한 최소 변경 작업을 계산하는 것
- 가능한 모든 조합을 계산하여 최댓값을 구한 후, 그리드 전체 크기에서 이 값을 빼면 필요한 최소 변경 작업의 개수를 얻음
예시 [[1, 2, 2], [1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0]]
const grid = [
[1, 2, 2],
[1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0]
];1. 초기 변수 설정
- cntY = [0, 0, 0]
- cntX = [0, 0, 0]
- n = 2 (grid.length - 1)
- n2 = 1 (n / 2)
2. 전체 그리드 숫자 개수 카운팅
for (let x = 0; x <= n; x++)
for (let y = 0; y <= n; y++)
cntX[grid[y][x]]++;
cntX = [2, 4, 3]
- 0의 개수: 2개
- 1의 개수: 4개
- 2의 개수: 3개
3. 'Y' 모양의 숫자 개수 카운팅
cntY[grid[n2][n2]]++;
for (let i = 0; i < n2; i++)
cntY[grid[i][i]]++,
cntY[grid[i][n - i]]++,
cntY[grid[n - i][n2]]++;
- grid[n2][n2]는 'Y' 모양의 중앙에 해당하는 요소
- 예제 그리드에서 grid[1][1]는 1
- cntY[1]++ --> cntY = [0, 1, 0]
- 대각선 및 중앙 세로줄 요소 카운팅:
- n2는 1이므로 i는 0에서 0까지 반복
- 첫 번째 대각선 요소 (좌상단에서 우하단):
- i = 0일 때, grid[0][0]는 1
- cntY[1]++ --> cntY = [0, 2, 0]
- 두 번째 대각선 요소 (우상단에서 좌하단):
- i = 0일 때, grid[0][2]는 2
- cntY[2]++ --> cntY = [0, 2, 1]
- 중앙 세로줄 요소:
- i = 0일 때, grid[2][1]는 1
- cntY[1]++ --> cntY = [0, 3, 1]
4. 'Y' 모양의 숫자 개수를 전체 그리드 숫자 개수에서 차감
- cntX = [3 - 0, 4 - 3, 2 - 1] --> cntX = [3, 1, 1]
왜 차감이 필요한가?
- 'Y' 모양 제외:
- 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 'Y' 모양에 해당하는 숫자들을 이미 카운팅했으므로, 전체 그리드 숫자 카운트에서 이를 제외해야 함.
- 'Y' 모양에 속하는 숫자들을 제외하지 않으면, 전체 그리드에서 중복 카운팅이 됨.
- 나머지 그리드 숫자 고려:
- 이제 남은 숫자들을 사용하여 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 몇 번의 변경 작업이 필요한지 계산할 수 있음.
- 차감 후의 cntX 배열은 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 사용할 수 있는 숫자들의 개수를 나타냄
5. 최소 변경 작업 계산
- 가능한 모든 조합을 계산하여 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 필요한 최소 변경 작업 수를 구함.
- 그리드의 전체 크기에서 최대한 'Y' 모양에 맞출 수 있는 숫자 조합의 개수를 빼줌.
- 최종 결과는 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 필요한 최소 변경 작업의 수
const max = Math.max(
cntY[0] + cntX[1], cntY[0] + cntX[2],
cntY[1] + cntX[0], cntY[1] + cntX[2],
cntY[2] + cntX[0], cntY[2] + cntX[1],
);
return (n + 1) ** 2 - max;
각 조합의 계산 결과:
- cntY[0] + cntX[1] = 0 + 1 = 1
- cntY[0] + cntX[2] = 0 + 1 = 1
- cntY[1] + cntX[0] = 3 + 3 = 6
- cntY[1] + cntX[2] = 3 + 1 = 4
- cntY[2] + cntX[0] = 1 + 3 = 4
- cntY[2] + cntX[1] = 1 + 1 = 2
최댓값 max = 6
return (n + 1) ** 2 - max;와 같은 수식을 사용하는 이유
- 그리드의 전체 크기 계산:
- (n + 1) ** 2는 그리드의 전체 셀 수를 나타냄
- 예를 들어, n = 2인 3x3 그리드에서는 (2 + 1) ** 2 = 3 ** 2 = 9로 전체 셀 수가 9개
- 최대로 맞출 수 있는 숫자의 개수:
- max는 가능한 조합 중에서 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 최대한으로 맞출 수 있는 숫자의 개수를 나타냄
- 이는 cntY와 cntX의 조합을 통해 계산됨.
- 최소 변경 작업 수 계산:
- 전체 셀 수 - 최대 맞출 수 있는 숫자의 개수는 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 필요한 최소 변경 작업 수를 의미.
- 전체 셀 수에서 최대한 맞출 수 있는 숫자의 개수를 빼면, 나머지 셀들을 'Y' 모양으로 바꾸기 위해 몇 번의 변경 작업이 필요한지 알 수 있음
따라서, 'Y' 모양을 만들기 위해 필요한 최소 변경 작업의 수는 9 - 6 = 3
'LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 435. Non-overlapping Intervals / TypeScript (0) | 2024.08.15 |
|---|---|
| 2966. Divide Array Into Arrays With Max Difference (0) | 2024.08.13 |
| 3192. Minimum Operations to Make Binary Array Elements Equal to One II / TypeScript (0) | 2024.07.26 |
| 646. Maximum Length of Pair Chain / TypeScript (4) | 2024.07.24 |
| 3211. Generate Binary Strings Without Adjacent Zeros / TypeScript (0) | 2024.07.23 |